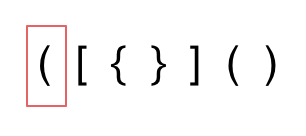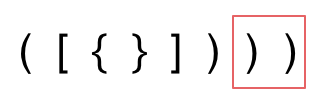栈和队列 1. 理论基础 栈是以底层容器完成其所有的工作,对外提供统一的接口,底层容器是可插拔的(也就是说我们可以控制使用哪种容器来实现栈的功能)。
2. 用栈实现队列 232.请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
你 只能 使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 输入: ["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"] [[], [1], [2], [], [], []] 输出: [null, null, null, 1, 1, false] 解释: MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue(); myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1] myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue) myQueue.peek(); // return 1 myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2] myQueue.empty(); // return false
思路 使用栈来模式队列的行为,如果仅仅用一个栈,是一定不行的,所以需要两个栈一个输入栈,一个输出栈 ,这里要注意输入栈和输出栈的关系。
下面动画模拟以下队列的执行过程:
执行语句:注意此时的输出栈的操作 注意此时的输出栈的操作
但在pop的时候,操作就复杂一些,输出栈如果为空,就把进栈数据全部导入进来(注意是全部导入) ,再从出栈弹出数据,如果输出栈不为空,则直接从出栈弹出数据就可以了。
最后如何判断队列为空呢?如果进栈和出栈都为空的话,说明模拟的队列为空了。
在代码实现的时候,会发现pop() 和 peek()两个函数功能类似,代码实现上也是类似的,可以思考一下如何把代码抽象一下
代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 var MyQueue = function ( this .stackIn = []; this .stackOut = []; }; MyQueue .prototype push = function (x ) { this .stackIn .push (x); }; MyQueue .prototype pop = function ( const size = this .stackOut .length ; if (size) { return this .stackOut .pop (); } while (this .stackIn .length ) { this .stackOut .push (this .stackIn .pop ()); } return this .stackOut .pop (); }; MyQueue .prototype peek = function ( const x = this .pop (); this .stackOut .push (x); return x; }; MyQueue .prototype empty = function ( return !this .stackIn .length && !this .stackOut .length };
3. 用队列实现栈 225.请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
注意:
你只能使用队列的基本操作 —— 也就是 push to back、peek/pop from front、size 和 is empty 这些操作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 输入: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 9 输出: 4 解释: 9 出现在 nums 中并且下标为 4输入: ["MyStack", "push", "push", "top", "pop", "empty"] [[], [1], [2], [], [], []] 输出: [null, null, null, 2, 2, false] 解释: MyStack myStack = new MyStack(); myStack.push(1); myStack.push(2); myStack.top(); // 返回 2 myStack.pop(); // 返回 2 myStack.empty(); // 返回 False
思路 根据题意,要用两个队列来实现栈,首先我们知道,队列是先进先出,栈是后进先出。
知道了以上要点,我们两个队列的用处也就一目了然了。
一个队列为主队列,一个为辅助队列,当入栈操作时,我们先将主队列内容导入辅助队列,然后将入栈元素放入主队列队头位置,再将辅助队列内容,依次添加进主队列即可。
代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 var MyStack = function ( this .queue1 = []; this .queue2 = []; }; MyStack .prototype push = function (x ) { this .queue1 .push (x); }; MyStack .prototype pop = function ( if (!this .queue1 .length ) { [this .queue1 , this .queue2 ] = [this .queue2 , this .queue1 ]; } while (this .queue1 .length > 1 ) { this .queue2 .push (this .queue1 .shift ()); } return this .queue1 .shift (); }; MyStack .prototype top = function ( const x = this .pop (); this .queue1 .push (x); return x; }; MyStack .prototype empty = function ( return !this .queue1 .length && !this .queue2 .length ; };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 var MyStack = function ( this .queue = []; }; MyStack .prototype push = function (x ) { this .queue .push (x); }; MyStack .prototype pop = function ( let size = this .queue .length ; while (size-- > 1 ) { this .queue .push (this .queue .shift ()); } return this .queue .shift (); }; MyStack .prototype top = function ( const x = this .pop (); this .queue .push (x); return x; }; MyStack .prototype empty = function ( return !this .queue .length ; };
4. 有效的括号 20.给定一个只包括 ‘(‘,’)’,’{‘,’}’,’[‘,’]’ 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 输入: ["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"] [[], [1], [2], [], [], []] 输出: [null, null, null, 1, 1, false] 解释: MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue(); myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1] myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue) myQueue.peek(); // return 1 myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2] myQueue.empty(); // return false
思路 先来分析一下 这里有三种不匹配的情况,
第一种情况,字符串里左方向的括号多余了 ,所以不匹配。
第二种情况,括号没有多余,但是 括号的类型没有匹配上。
第三种情况,字符串里右方向的括号多余了,所以不匹配。
我们的代码只要覆盖了这三种不匹配的情况,就不会出问题,可以看出 动手之前分析好题目的重要性。
动画如下:
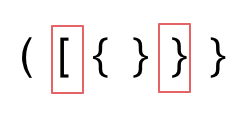
第一种情况:已经遍历完了字符串,但是栈不为空,说明有相应的左括号没有右括号来匹配,所以return false
第二种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,发现栈里没有要匹配的字符。所以return false
第三种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,栈已经为空了,没有匹配的字符了,说明右括号没有找到对应的左括号return false
那么什么时候说明左括号和右括号全都匹配了呢,就是字符串遍历完之后,栈是空的,就说明全都匹配了。
代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 var isValid = function (s ) { const stack = [], map = { "(" :")" , "{" :"}" , "[" :"]" }; for (const x of s) { if (x in map) { stack.push (x); continue ; }; if (map[stack.pop ()] !== x) return false ; } return !stack.length ; };
5. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项 给出由小写字母组成的字符串 S,重复项删除操作会选择两个相邻且相同的字母,并删除它们。
在 S 上反复执行重复项删除操作,直到无法继续删除。
在完成所有重复项删除操作后返回最终的字符串。答案保证唯一。
1 2 3 4 输入:"abbaca" 输出:"ca" 解释: 例如,在 "abbaca" 中,我们可以删除 "bb" 由于两字母相邻且相同,这是此时唯一可以执行删除操作的重复项。之后我们得到字符串 "aaca",其中又只有 "aa" 可以执行重复项删除操作,所以最后的字符串为 "ca"。
思路 本题也是用栈来解决的经典题目。
那么栈里应该放的是什么元素呢?
我们在删除相邻重复项的时候,其实就是要知道当前遍历的这个元素,我们在前一位是不是遍历过一样数值的元素,那么如何记录前面遍历过的元素呢?
所以就是用栈来存放,那么栈的目的,就是存放遍历过的元素,当遍历当前的这个元素的时候,去栈里看一下我们是不是遍历过相同数值的相邻元素。
然后再去做对应的消除操作。 如动画所示:
从栈中弹出剩余元素,此时是字符串ac,因为从栈里弹出的元素是倒序的,所以再对字符串进行反转一下,就得到了最终的结果。
代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 var removeDuplicates = function (s ) {const result = [] for (const i of s){ if (i === result[result.length -1 ]){ result.pop () }else { result.push (i) } } return result.join ('' ) };
6. 逆波兰表达式求值
给你一个字符串数组 tokens ,表示一个根据 逆波兰表示法 表示的算术表达式。
请你计算该表达式。返回一个表示表达式值的整数。
注意:
有效的算符为 ‘+’、’-‘、’*’ 和 ‘/‘ 。
每个操作数(运算对象)都可以是一个整数或者另一个表达式。
两个整数之间的除法总是 向零截断 。
表达式中不含除零运算。
输入是一个根据逆波兰表示法表示的算术表达式。
答案及所有中间计算结果可以用 32 位 整数表示。
1 2 3 输入:tokens = ["2","1","+","3","*"] 输出:9 解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:((2 + 1) * 3) = 9
1 2 3 输入:tokens = ["4","13","5","/","+"] 输出:6 解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:(4 + (13 / 5)) = 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 输入:tokens = ["10","6","9","3","+","-11","*","/","*","17","+","5","+"] 输出:22 解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为: ((10 * (6 / ((9 + 3) * -11))) + 17) + 5 = ((10 * (6 / (12 * -11))) + 17) + 5 = ((10 * (6 / -132)) + 17) + 5 = ((10 * 0) + 17) + 5 = (0 + 17) + 5 = 17 + 5 = 22
思路 逆波兰表达式:是一种后缀表达式,所谓后缀就是指运算符写在后面。
平常使用的算式则是一种中缀表达式,如 ( 1 + 2 ) * ( 3 + 4 ) 。
该算式的逆波兰表达式写法为 ( ( 1 2 + ) ( 3 4 + ) * ) 。
逆波兰表达式主要有以下两个优点:
本题中每一个子表达式要得出一个结果,然后拿这个结果再进行运算,那么这岂不就是一个相邻字符串消除的过程,和删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项 中的对对碰游戏是不是就非常像了。
如动画所示:
代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 var evalRPN = function (tokens ) { const stack = []; for (const token of tokens) { if (isNaN (Number (token))) { const n2 = stack.pop (); const n1 = stack.pop (); switch (token) { case "+" : stack.push (n1 + n2); break ; case "-" : stack.push (n1 - n2); break ; case "*" : stack.push (n1 * n2); break ; case "/" : stack.push (n1 / n2 | 0 ); break ; } } else { stack.push (Number (token)); } } return stack[0 ]; };
7. 滑动窗口最大值 给你一个整数数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。
返回 滑动窗口中的最大值 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 输入:nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], k = 3 输出:[3,3,5,5,6,7] 解释: 滑动窗口的位置 最大值 --------------- ----- [1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3 1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3 1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5 1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5 1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6 1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
1 2 输入:nums = [1], k = 1 输出:[1]
思路 维护单调递减队列,当进入滑动窗口的元素大于等于队尾的元素时 不断从队尾出队,直到进入滑动窗口的元素小于队尾的元素,才可以入队,以保证单调递减的性质,当队头元素已经在滑动窗口外了,移除对头元素,当i大于等于k-1的时候,单调递减队头就是滑动窗口的最大值
代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 var maxSlidingWindow = function (nums, k ) { const q = []; const ans = []; for (let i = 0 ; i < nums.length ; i++) { while (q.length && nums[i] >= nums[q[q.length - 1 ]]) { q.pop (); } q.push (i); while (q[0 ] <= i - k) { q.shift (); } if (i >= k - 1 ) ans.push (nums[q[0 ]]); } return ans; };
8. 前 K 个高频元素 给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你返回其中出现频率前 k 高的元素。你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。
1 2 输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2 输出: [1,2]
1 2 输入: nums = [1], k = 1 输出: [1]
思路 寻找前k个最大元素流程如图所示:(图中的频率只有三个,所以正好构成一个大小为3的小顶堆,如果频率更多一些,则用这个小顶堆进行扫描)
代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 let topKFrequent = function (nums, k ) { let map = new Map (), arr = [...new Set (nums)] nums.map ((num ) => { if (map.has (num)) map.set (num, map.get (num)+1 ) else map.set (num, 1 ) }) return arr.sort ((a, b ) => map.get (b) - map.get (a)).slice (0 , k); };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 let topKFrequent = function (nums, k ) { let map = new Map (), heap = [,] nums.map ((num ) => { if (map.has (num)) map.set (num, map.get (num)+1 ) else map.set (num, 1 ) }) if (map.size <= k) { return [...map.keys ()] } let i = 0 map.forEach ((value, key ) => { if (i < k) { heap.push (key) if (i === k-1 ) buildHeap (heap, map, k) } else if (map.get (heap[1 ]) < value) { heap[1 ] = key heapify (heap, map, k, 1 ) } i++ }) heap.shift () return heap }; let buildHeap = (heap, map, k ) => { if (k === 1 ) return for (let i = Math .floor (k/2 ); i>=1 ; i--) { heapify (heap, map, k, i) } } let heapify = (heap, map, k, i ) => { while (true ) { let minIndex = i if (2 *i <= k && map.get (heap[2 *i]) < map.get (heap[i])) { minIndex = 2 *i } if (2 *i+1 <= k && map.get (heap[2 *i+1 ]) < map.get (heap[minIndex])) { minIndex = 2 *i+1 } if (minIndex !== i) { swap (heap, i, minIndex) i = minIndex } else { break } } } let swap = (arr, i , j ) => { let temp = arr[i] arr[i] = arr[j] arr[j] = temp }
 在push数据的时候,只要数据放进输入栈就好,但在pop的时候,操作就复杂一些,输出栈如果为空,就把进栈数据全部导入进来(注意是全部导入),再从出栈弹出数据,如果输出栈不为空,则直接从出栈弹出数据就可以了。
在push数据的时候,只要数据放进输入栈就好,但在pop的时候,操作就复杂一些,输出栈如果为空,就把进栈数据全部导入进来(注意是全部导入),再从出栈弹出数据,如果输出栈不为空,则直接从出栈弹出数据就可以了。